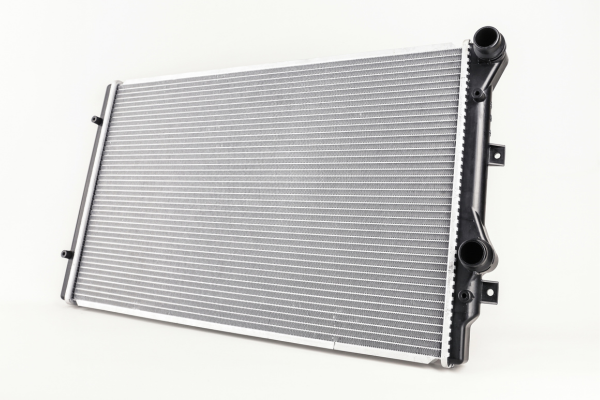


The radiator is a central component of a vehicle’s cooling system. It regulates the engine’s temperature and prevents it from overheating. As the coolant travels through the radiator’s small channels, it cools down, bringing it to an optimal temperature to help cool the engine block. Once in the engine block, the coolant absorbs the excess heat and brings it back to the radiator, where it cools down once again. A simple but critical cycle.
Scroll to learn more about coolant related issues.
Rust accumulation
Faulty radiator cap
 Damaged
Damaged Normal
NormalTransmission cooler issue
 Damaged
Damaged Normal
NormalDamaged Radiator Cap
 Damaged
Damaged Normal
Normal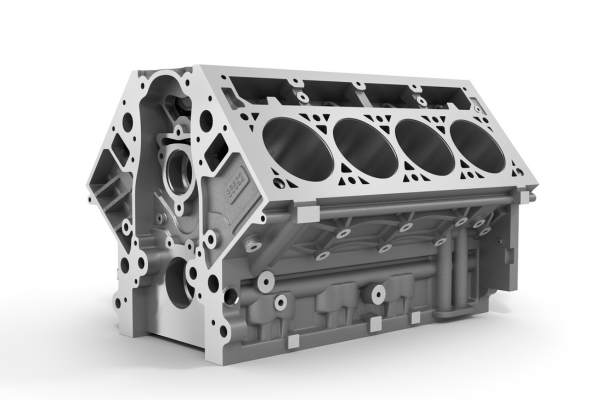
An engine block, or cylinder block, acts as a structural framework for all the essential components required for combustion including pistons, cylinder heads, camshafts, valves, crankshafts, oil galleries and coolant passages. As the engine block is a core component for any vehicle, it is designed for durability to tolerate high-temperature & pressure. If the engine block is damaged, you will most likely have to replace it since repairing can be a tough feat.
Scroll to learn more about coolant related issues.
Cracked engine block causes leaks into engine cylinders and burns
Head gasket damage
 Damaged
Damaged Normal
NormalCoolant leaks due to cracked engine block
Coolant-oil intermix due to crack between oil and coolant passages
 Damaged
Damaged Normal
NormalCracked engine block causes coolant to leak and burn when in contact with engine’s external surface
 Damaged
Damaged Normal
Normal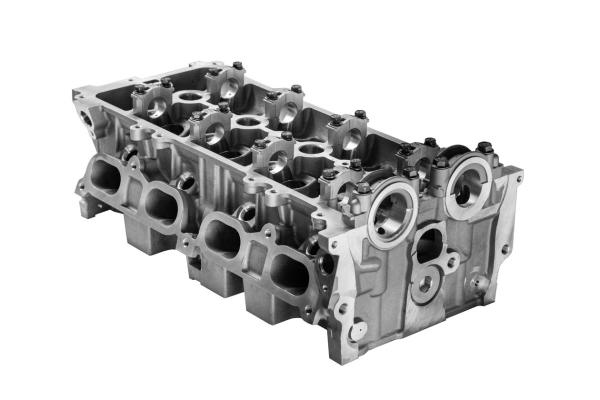
The cylinder head is a three-piece assembly, part of the combustion chamber, and consisting of a lower member that contains the gas passages, a mounting for the injector valves and the ignition plug. The cylinder head itself is a piston-like member retained by a flange and eight screws to the lower member of the chamber. The cylinder head mounts on the cylinder block (engine housing) and needs to be continuously cooled.
Scroll to learn more about coolant related issues.
Coolant levels drop due to a crack from overstressing
Missing/bad foaming agents
 Damaged
Damaged Normal
NormalExtreme pressure & temperatures
 Damaged
Damaged Normal
NormalOil & coolant leaks due to cracks
 Damaged
Damaged Normal
NormalMixture in the chamber does not burn properly due to crack
 Damaged
Damaged Normal
Normal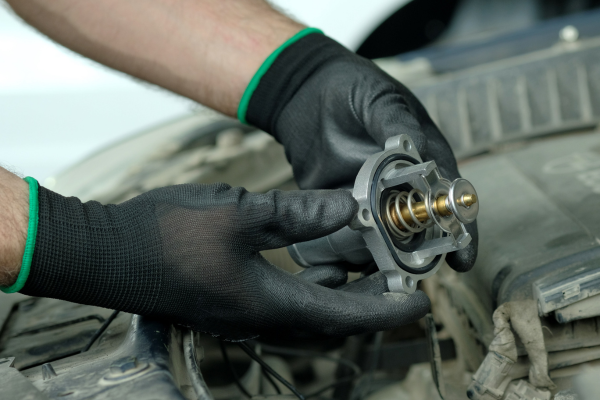
The thermostat is responsible for regulating coolant flow through the engine. If the engine is cold, the thermostat stays closed to let the engine warm up. As the engine heats up, the thermostat gradually opens, allowing coolant to reach the radiator to bring the engine to its optimal temperature. If the thermostats begins to fail, the engine could overheat or overcool, and it could lead to costly repairs.
Scroll to learn more about coolant related issues.
Corrosion or clog blocks thermostat in closed/open position
 Damaged
Damaged Normal
NormalDamaged thermostat housing gasket
 Damaged
Damaged Normal
Normal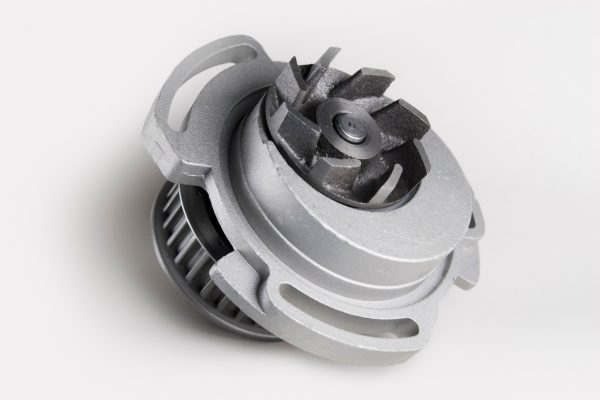
The “water” pump is responsible for pushing coolant through the engine to help regulate its temperature. It helps ensure the motor remains at a constant temperature, no matter the weather or the strain put on it.
Scroll to learn more about coolant related issues.
Water pump no longer working
 Damaged
Damaged Normal
NormalEroded/cracked/loose gasket
 Damaged
Damaged Normal
NormalEroded/cracked bearings
 Damaged
Damaged Normal
NormalAir seeps into the system and causes corrosion inside the pump
 Damaged
Damaged Normal
Normal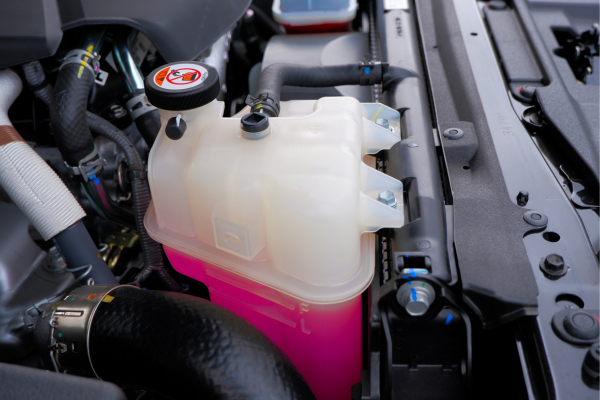
The vehicle’s hoses are made of flexible rubber composites that handle vibrations from the engine. Hoses are designed to withstand coolant under intense pressure, extreme temperatures, oils, dirt, and sludge.
The coolant reservoirs are a storage tank for excess engine coolant and allow engine coolant to flow in and out per the needs of the cooling systems. As the engine coolant temperature rises, the coolant expands, and the radiator cap as well as the plastic reservoir walls allow excess pressure to bleed off.
Scroll to learn more about coolant related issues.
Bad thermal regulation leads to drying out & cracks
 Damaged
Damaged Normal
Normal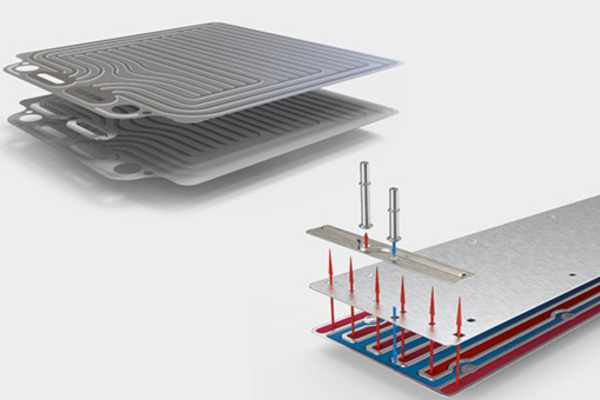
EV battery cooling plates regulate the temperature of the battery pack and some of the electronics by circulating coolant between two thin aluminum (Al) sheets. Battery fluid goes through tubes, cold plates, or other components that surround the battery cells and carry heat to another location, such as a radiator or a heat exchanger. Battery plates carrying the liquid prevent direct electrical contact between the cells and the liquid coolant.
Damage to an EV coolant system often results in costly battery system replacement.
Scroll to learn more about coolant related issues.
Cooling plate corrode and crack
Debris/impurities present in the battery fluid accumulates in the small channels
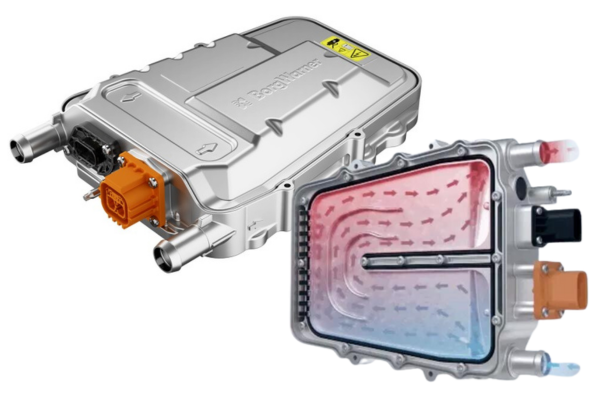
High Voltage Coolant Heaters have been developed to keep the core components of hybrid and pure electric vehicles at an optimal temperature, improving charging efficiency, durability and driving range. This heating system delivers heat to the vehicle interior and helps clears the ice from windows quickly.
Scroll to learn more about coolant related issues.
Cooling plate corrode and crack
Air bubbles form, causing foaming

The condenser’s role is essentially that of a heat exchanger, passing refrigerant through a large block where it transfers the thermal properties of the cryogen to other parts of the cooling system. The condenser is where the hot liquid refrigerant transfers its heat to the coolant, which then carries it to the radiator.
Scroll to learn more about coolant related issues.
Cooling plate corrode and crack
Air bubbles form in the HVCH and cause foaming
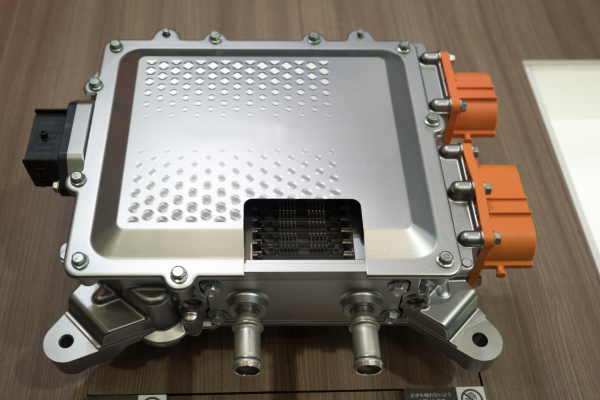

An inverter is an electrical device that converts sourced electricity from DC (Direct Current) to AC (Alternating Current). DC power is fed to the primary winding in a transformer within the inverter housing. Through an electronic switch, the current’s direction flow is continuously and periodically reversed. The in/outflow of electricity produces AC current in the transformer’s secondary winding circuit. Ultimately, this induced alternating current electricity provides power for an AC load—for example, an electric vehicle’s (EV) traction motor.
Scroll to learn more about coolant related issues.
Cooling plate corrode and crack
Air bubbles form, causing foaming



